just_audio
just_audio 是一款功能丰富的音频播放器,适用于 Android、iOS、macOS 和 Web。
混合搭配音频插件
Flutter 插件生态系统包含各种有用的音频插件。为了让这些插件在单个应用中协同工作,just_audio 仅负责播放音频。通过专注于单一职责,不同的音频插件可以安全地协同工作,而不会因为职责重叠而导致运行时冲突。
其他常见的音频功能由单独的插件提供(可选)
- just_audio_background:使用此插件可让您的应用在后台播放音频,并响应锁屏、媒体通知、耳机、AndroidAuto/CarPlay 或智能手表上的控件。
- audio_service:如果您的应用有更高级的后台音频需求,而 `just_audio_background` 无法满足,请使用此插件。
- audio_session:使用此插件可配置和管理您的应用如何与其他音频应用(例如电话呼叫或导航器中断)进行交互。
- just_waveform:使用此插件可提取音频文件的波形,适用于视觉渲染。
对即将推出的功能进行投票
点击您想投票的 GitHub issue 上的“点赞”图标。
- 音高转换:#329
- 均衡器:#147
- 投屏支持(Chromecast 和 AirPlay):#211
- 音量增强和跳过静音:#307
- 所有功能请求按受欢迎程度排序
如果您希望为项目带来更多动力,也请考虑在 此页面(pub.dev)的顶部按下“点赞”按钮。更多的用户会带来更多的 bug 报告和功能请求,从而提高稳定性和功能性。
鸣谢
本项目得到了 GitHub 贡献者和赞助者们出色的开源社区支持。谢谢!
- libwinmedia 支持了 Windows 和 Linux 的实现。
功能
| 功能 | Android | iOS | macOS | Web | Windows | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从 URL 读取 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 从文件读取 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 从资源读取 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 从字节流读取 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| 请求头 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |||
| DASH | ✅ | ✅ | ||||
| HLS | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| ICY 元数据 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |||
| 缓冲状态/位置 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 播放/暂停/跳转 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 设置音量/速度 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 剪辑音频 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| 播放列表 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 循环/随机播放 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 组合音频 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| 无缝播放 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| 报告播放器错误 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 处理电话中断 | ✅ | ✅ | ||||
| 缓冲/加载选项 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |||
| 设置音高 | ✅ | |||||
| 跳过静音 | ✅ | |||||
| 均衡器 | ✅ | |||||
| 音量增强 | ✅ |
实验性功能
| 功能 | Android | iOS | macOS | Web |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 同步下载+缓存 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| 波形可视化器(参见 #97) | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| FFT 可视化器(参见 #97) | ✅ | |||
| 后台 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
请考虑在此 处 报告您遇到的任何 bug,或在此 处 提交拉取请求。
从 0.5.x 迁移到 0.6.x
`load()` 和 `stop()` 在 0.6.x 中有了新的行为,详细记录在 此处,它提供了更大的灵活性来获取和释放系统资源。要快速迁移并保持 0.5.x 的行为,请执行以下操作:
- 将 `await player.load(source);` 替换为 `await player.setAudioSource(source);`
- 将 `await stop();` 替换为 `await player.pause(); await player.seek(Duration.zero);`
教程
- @mvolpato 著 创建一个简单的 Flutter 音乐播放器应用
- @suragch 著 使用 Just Audio 在 Flutter 中播放短音频片段
- @suragch 著 使用 Just Audio 在 Flutter 中流式传输音频
- @suragch 著 使用 Just Audio 在 Flutter 中管理播放列表
示例
初始化
final player = AudioPlayer();
var duration = await player.setUrl('https://foo.com/bar.mp3');
var duration = await player.setFilePath('/path/to/file.mp3');
var duration = await player.setAsset('path/to/asset.mp3');
设置 HTTP 用户代理
final player = AudioPlayer(
userAgent: 'myradioapp/1.0 (Linux;Android 11) https://myradioapp.com',
);
请求头
var duration = await player.setUrl('https://foo.com/bar.mp3',
headers: {'header1': 'value1', 'header2': 'value2'});
标准控件
player.play(); // Usually you don't want to wait for playback to finish.
await player.seek(Duration(seconds: 10));
await player.pause();
剪辑音频
await player.setClip(start: Duration(seconds: 10), end: Duration(seconds: 20));
await player.play(); // Waits until the clip has finished playing
调整音频
await player.setSpeed(2.0); // Double speed
await player.setVolume(0.5); // Halve volume
无缝播放列表
await player.setAudioSource(
ConcatenatingAudioSource(
// Start loading next item just before reaching it.
useLazyPreparation: true, // default
// Customise the shuffle algorithm.
shuffleOrder: DefaultShuffleOrder(), // default
// Specify the items in the playlist.
children: [
AudioSource.uri(Uri.parse("https://example.com/track1.mp3")),
AudioSource.uri(Uri.parse("https://example.com/track2.mp3")),
AudioSource.uri(Uri.parse("https://example.com/track3.mp3")),
],
),
// Playback will be prepared to start from track1.mp3
initialIndex: 0, // default
// Playback will be prepared to start from position zero.
initialPosition: Duration.zero, // default
);
await player.seekToNext();
await player.seekToPrevious();
// Jump to the beginning of track3.mp3.
await player.seek(Duration(milliseconds: 0), index: 2);
循环和随机播放
await player.setLoopMode(LoopMode.off); // no looping (default)
await player.setLoopMode(LoopMode.all); // loop playlist
await player.setLoopMode(LoopMode.one); // loop current item
await player.setShuffleModeEnabled(true); // shuffle playlist
组合音频源
player.setAudioSource(
// Loop child 4 times
LoopingAudioSource(
count: 4,
// Play children one after the other
child: ConcatenatingAudioSource(
children: [
// Play a regular media file
ProgressiveAudioSource(Uri.parse("https://example.com/foo.mp3")),
// Play a DASH stream
DashAudioSource(Uri.parse("https://example.com/audio.mdp")),
// Play an HLS stream
HlsAudioSource(Uri.parse("https://example.com/audio.m3u8")),
// Play a segment of the child
ClippingAudioSource(
child: ProgressiveAudioSource(Uri.parse("https://w.xyz/p.mp3")),
start: Duration(seconds: 25),
end: Duration(seconds: 30),
),
],
),
),
);
管理资源
// Set the audio source but manually load audio at a later point.
await player.setUrl('https://a.b/c.mp3', preload: false);
// Acquire platform decoders and start loading audio.
var duration = await player.load();
// Unload audio and release decoders until needed again.
await player.stop();
// Permanently release decoders/resources used by the player.
await player.dispose();
捕获播放器错误
try {
await player.setUrl("https://s3.amazonaws.com/404-file.mp3");
} on PlayerException catch (e) {
// iOS/macOS: maps to NSError.code
// Android: maps to ExoPlayerException.type
// Web: maps to MediaError.code
// Linux/Windows: maps to PlayerErrorCode.index
print("Error code: ${e.code}");
// iOS/macOS: maps to NSError.localizedDescription
// Android: maps to ExoPlaybackException.getMessage()
// Web/Linux: a generic message
// Windows: MediaPlayerError.message
print("Error message: ${e.message}");
} on PlayerInterruptedException catch (e) {
// This call was interrupted since another audio source was loaded or the
// player was stopped or disposed before this audio source could complete
// loading.
print("Connection aborted: ${e.message}");
} catch (e) {
// Fallback for all errors
print(e);
}
监听状态变化
player.playerStateStream.listen((state) {
if (state.playing) ... else ...
switch (state.processingState) {
case ProcessingState.idle: ...
case ProcessingState.loading: ...
case ProcessingState.buffering: ...
case ProcessingState.ready: ...
case ProcessingState.completed: ...
}
});
// See also:
// - durationStream
// - positionStream
// - bufferedPositionStream
// - sequenceStateStream
// - sequenceStream
// - currentIndexStream
// - icyMetadataStream
// - playingStream
// - processingStateStream
// - loopModeStream
// - shuffleModeEnabledStream
// - volumeStream
// - speedStream
// - playbackEventStream
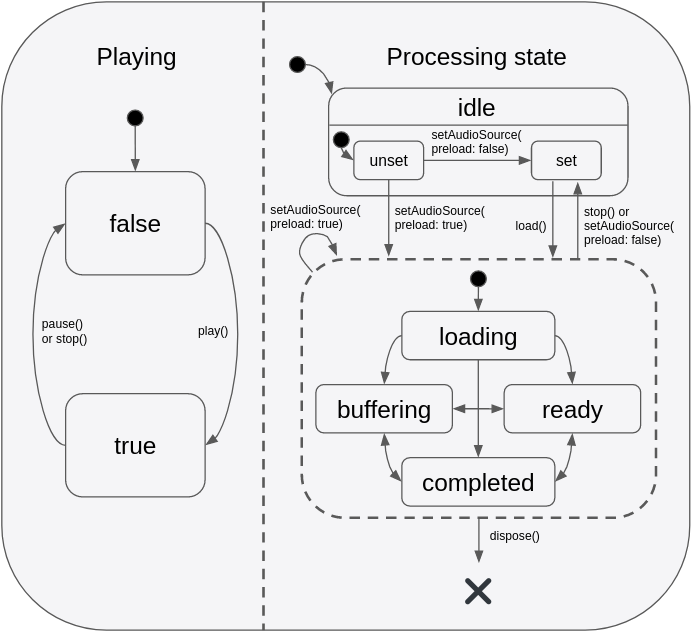
状态模型
播放器的状态由两个独立的状态组成:`playing` 和 `processingState`。`playing` 状态通常映射到应用的播放/暂停按钮,并且仅在响应应用程序的直接方法调用时才会更改。相比之下,`processingState` 反映了底层音频解码器的状态,它既可以响应应用程序的方法调用而改变,也可以响应音频处理管道中异步发生的事件而改变。下图描绘了有效状态转换。
此状态模型提供了一种灵活的方式来捕获状态的不同组合,例如 playing+buffering 与 paused+buffering,从而可以更准确地在应用的 UI 中表示状态。重要的是要理解,即使 `playing == true`,除非 `processingState == ready`(表示缓冲区已满并准备好播放),否则不会发出任何声音。当想象 `playing` 状态映射到应用的播放/暂停按钮时,这在直观上是合理的。
- 当用户按下“播放”开始新曲目时,按钮会立即反映“播放”状态的变化,尽管在音频加载期间(`processingState == loading`)会有几秒钟的静音,但一旦缓冲区最终填满(即 `processingState == ready`),音频播放就会开始。
- 当播放过程中发生缓冲时(例如由于网络连接缓慢),应用的播放/暂停按钮仍保持 `playing` 状态,尽管暂时听不到声音(`processingState == buffering`)。一旦缓冲区再次填满(`processingState == ready`),声音将再次可用。
- 当播放到达音频流末尾时,播放器保持 `playing` 状态,并且搜寻条位于曲目末尾。在应用程序将播放位置搜寻到流的早期点之前,将听不到任何声音。一些应用可能会选择在此处显示一个“重播”按钮来替换播放/暂停按钮,该按钮调用 `seek(Duration.zero)`。点击后,播放将自动从搜寻点继续(因为它根本从未暂停过)。其他应用可能更希望监听 `processingState == completed` 事件,并在该点以编程方式暂停和倒带音频。
希望通过单个组合流响应这两个独立状态的应用可以监听 `playerStateStream`。此流将发出包含 `playing` 和 `processingState` 最新值的事件。
配置音频会话
如果您的应用使用音频,您应该告知操作系统您的应用的使用场景以及您的应用将如何与其他设备上的音频应用进行交互。不同的音频应用通常有独特的需求。例如,当导航应用播报驾驶指令时,音乐播放器应该降低其音量,而播客播放器应该暂停其音频。根据您正在构建的这三个应用中的哪一个,您需要配置您应用的音频设置和回调以适当地处理这些交互。
默认情况下,just_audio 将选择适合音乐播放器应用的设置,这意味着当导航器开始播报时,它会自动降低音频音量,但在电话呼叫或另一个音乐播放器开始时会暂停。如果您正在构建播客播放器或有声读物阅读器,此行为将不合适。虽然用户可以在后台播放音乐时理解导航说明,但同时收听有声读物或播客时理解导航说明会更加困难。
您可以使用 audio_session 包来更改您应用默认的音频会话配置。例如,对于播客播放器,您可以使用
final session = await AudioSession.instance;
await session.configure(AudioSessionConfiguration.speech());
注意:如果您的应用使用了许多不同的音频插件,例如用于音频录制、文本转语音或后台音频,则这些插件可能会在内部覆盖彼此的音频会话设置,因此建议在所有其他音频插件加载后,使用 audio_session 应用您自己偏好的配置。您可以考虑要求您使用的每个音频插件的开发者提供一个选项,使其不覆盖这些全局设置,并允许其被外部管理。
平台特定配置
Android
为了让您的应用程序能够访问互联网上的音频文件,请将以下权限添加到您的 `AndroidManifest.xml` 文件中:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
如果您希望连接到非 HTTPS URL,还请将以下属性添加到 `application` 元素中:
<application ... android:usesCleartextTraffic="true">
如果您需要访问播放器的 `AudioSession` ID,您可以监听 `AudioPlayer.androidAudioSessionIdStream`。请注意,每次设置新的 `AudioAttributes` 时,`AudioSession` ID 都会更改。
iOS
使用默认配置,App Store 将会检测到您的应用使用了 AVAudioSession API,其中包含麦克风 API。出于隐私原因,它会要求您描述您的应用对麦克风的使用情况。如果您的应用确实使用了麦克风,您可以通过编辑 `Info.plist` 文件来描述您的使用情况,如下所示:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>... explain why the app uses the microphone here ...</string>
但如果您的应用不使用麦克风,您可以向 `ios/Podfile` 传递一个构建选项来“编译掉”任何麦克风代码,这样 App Store 就不会询问上述使用描述。为此,请如下编辑您的 `ios/Podfile`:
post_install do |installer|
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
flutter_additional_ios_build_settings(target)
# ADD THE NEXT SECTION
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings['GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS'] ||= [
'$(inherited)',
'AUDIO_SESSION_MICROPHONE=0'
]
end
end
end
如果您希望连接到非 HTTPS URL,请将以下内容添加到您的 `Info.plist` 文件中:
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoadsForMedia</key>
<true/>
</dict>
iOS 播放器依赖于服务器标头(例如 `Content-Type`、`Content-Length` 和 字节范围请求)来了解如何解码文件,并在适用时报告其持续时间。对于文件,iOS 依赖于文件扩展名。
macOS
为了让您的 macOS 应用程序能够访问互联网上的音频文件,请将以下内容添加到您的 `DebugProfile.entitlements` 和 `Release.entitlements` 文件中:
<key>com.apple.security.network.client</key>
<true/>
如果您希望连接到非 HTTPS URL,请将以下内容添加到您的 `Info.plist` 文件中:
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoadsForMedia</key>
<true/>
</dict>
macOS 播放器依赖于服务器标头(例如 `Content-Type`、`Content-Length` 和 字节范围请求)来了解如何解码文件,并在适用时报告其持续时间。对于文件,macOS 依赖于文件扩展名。
Windows
在 `pubspec.yaml` 文件中,将 just_audio_libwinmedia 依赖项与 `just_audio` 一起添加。
dependencies:
just_audio: any # substitute version number
just_audio_libwinmedia: any # substitute version number
Linux (未测试)
在 `pubspec.yaml` 文件中,将 just_audio_libwinmedia 依赖项与 `just_audio` 一起添加。
dependencies:
just_audio: any # substitute version number
just_audio_libwinmedia: any # substitute version number
相关插件
- audio_service:在后台播放任何音频,并通过锁屏、Android 通知、iOS 控制中心和耳机按钮控制播放。
- audio_session:配置您应用的音频类别(例如,音乐与语音),并配置您的应用如何与其他音频应用交互(例如,音频焦点、音量衰减、混合)。